Java相对路径读取文件
不管你是新手还是老鸟,在程序中读取资源文件总会遇到一些找不到文件的问题,这与Java底层的实现有关,不能算bug,只要方法得当,问题还是可以解决的。
项目的文件夹结构:
repathtest
├─src
│ └─com
│ └─lavasoft
│ ├─test
│ └─res
├─doc
├─src
│ └─com
│ └─lavasoft
│ ├─test
│ └─res
├─doc

1、在Java开发工具的project中使用相对路径
在project中,相对路径的根目录是project的根文件夹,在此就是repathtest文件夹了。
创建文件的写法是:
File f = new File("src/com/lavasoft/res/a.txt");
File f = new File("doc/b.txt");
注意:
路径不以“/”开头;
脱离了IDE环境,这个写法就是错误的,也并非每个IDE都如此,但我见到的都是这样的。
2、通过CLASSPATH读取包内文件
读取包内文件,使用的路径一定是相对的classpath路径,比如a,位于包内,此时可以创建读取a的字节流:
InputStream in = ReadFile.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/lavasoft/res/a.txt");
有了字节流,就能读取到文件内容了。
注意:
这里必须以“/”开头;
3、看看完整的测试代码
package com.lavasoft.test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* Java读取相对路径的文件
*
* @author leizhimin 2010-1-15 10:59:43
*/
public class ReadFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
readTextA_ByClassPath();
readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath();
readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath();
}
/**
* 通过工程相对路径读取(包内)文件,注意不以“/”开头
*/
public static void readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath() {
System.out.println("-----------------readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------");
File f = new File("src/com/lavasoft/res/a.txt");
String a = file2String(f, "GBK");
System.out.println(a);
}
/**
* 通过工程相对路径读取(包外)文件,注意不以“/”开头
*/
public static void readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath() {
System.out.println("-----------------readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------");
File f = new File("doc/b.txt");
String b = file2String(f, "GBK");
System.out.println(b);
}
/**
* 通过CLASSPATH读取包内文件,注意以“/”开头
*/
public static void readTextA_ByClassPath() {
System.out.println("-----------------readTextA_ByClassPath---------------------");
InputStream in = ReadFile.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/lavasoft/res/a.txt");
String a = stream2String(in, "GBK");
System.out.println(a);
}
/**
* 文件转换为字符串
*
* @param f 文件
* @param charset 文件的字符集
* @return 文件内容
*/
public static String file2String(File f, String charset) {
String result = null;
try {
result = stream2String(new FileInputStream(f), charset);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 文件转换为字符串
*
* @param in 字节流
* @param charset 文件的字符集
* @return 文件内容
*/
public static String stream2String(InputStream in, String charset) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
try {
Reader r = new InputStreamReader(in, charset);
int length = 0;
for (char[] c = new char[1024]; (length = r.read(c)) != -1;) {
sb.append(c, 0, length);
}
r.close();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
import java.io.*;
/**
* Java读取相对路径的文件
*
* @author leizhimin 2010-1-15 10:59:43
*/
public class ReadFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
readTextA_ByClassPath();
readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath();
readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath();
}
/**
* 通过工程相对路径读取(包内)文件,注意不以“/”开头
*/
public static void readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath() {
System.out.println("-----------------readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------");
File f = new File("src/com/lavasoft/res/a.txt");
String a = file2String(f, "GBK");
System.out.println(a);
}
/**
* 通过工程相对路径读取(包外)文件,注意不以“/”开头
*/
public static void readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath() {
System.out.println("-----------------readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------");
File f = new File("doc/b.txt");
String b = file2String(f, "GBK");
System.out.println(b);
}
/**
* 通过CLASSPATH读取包内文件,注意以“/”开头
*/
public static void readTextA_ByClassPath() {
System.out.println("-----------------readTextA_ByClassPath---------------------");
InputStream in = ReadFile.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/lavasoft/res/a.txt");
String a = stream2String(in, "GBK");
System.out.println(a);
}
/**
* 文件转换为字符串
*
* @param f 文件
* @param charset 文件的字符集
* @return 文件内容
*/
public static String file2String(File f, String charset) {
String result = null;
try {
result = stream2String(new FileInputStream(f), charset);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 文件转换为字符串
*
* @param in 字节流
* @param charset 文件的字符集
* @return 文件内容
*/
public static String stream2String(InputStream in, String charset) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
try {
Reader r = new InputStreamReader(in, charset);
int length = 0;
for (char[] c = new char[1024]; (length = r.read(c)) != -1;) {
sb.append(c, 0, length);
}
r.close();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
(代码写得粗糙,异常没做认真处理)
运行结果:
-----------------readTextA_ByClassPath---------------------
aaaaaaaaa
sssssssss
-----------------readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------
aaaaaaaaa
sssssssss
-----------------readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------
bbbbbbbbbbb
Process finished with exit code 0
aaaaaaaaa
sssssssss
-----------------readTextA_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------
aaaaaaaaa
sssssssss
-----------------readTextB_ByProjectRelativePath---------------------
bbbbbbbbbbb
Process finished with exit code 0
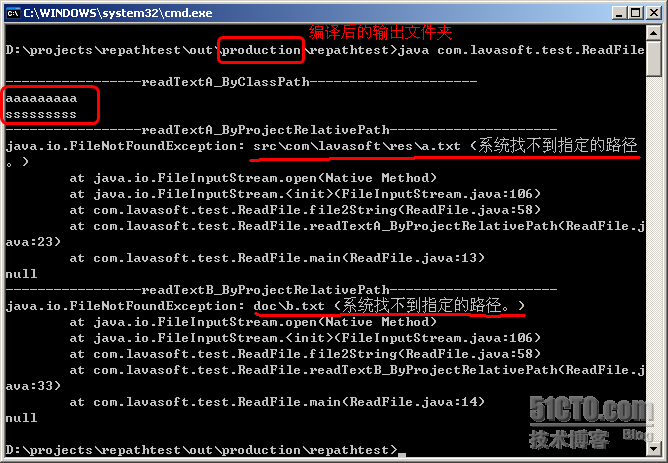
这是通过IDEA开发工具运行的,结果没问题,如果换成控制台执行,那么使用了项目相对路径的读取方式会失败,原因是,此时已经脱离了项目的开发环境,-----这个问题常常困扰着一些菜鸟,代码在开发工具好好的,发布后执行就失败了!
下面我截个图:
5、获取CLASSPATH下文件的绝对路径
当使用相对路径写入文件时候,就需要用到绝对路径。下面是个例子:
package com.lavasoft;
import java.io.File;
/**
* CLASSPATH文件的绝对路径获取测试
*
* @author leizhimin 2010-1-18 9:33:02
*/
public class Test {
//classpath的文件路径
private static String cp = "/com/lavasoft/cfg/syscfg.properties";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当前类的绝对路径
System.out.println(Test.class.getResource("/").getFile());
//指定CLASSPATH文件的绝对路径
System.out.println(Test.class.getResource(cp).getFile());
//指定CLASSPATH文件的绝对路径
File f = new File(Test.class.getResource(cp).getFile());
System.out.println(f.getPath());
}
}
import java.io.File;
/**
* CLASSPATH文件的绝对路径获取测试
*
* @author leizhimin 2010-1-18 9:33:02
*/
public class Test {
//classpath的文件路径
private static String cp = "/com/lavasoft/cfg/syscfg.properties";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当前类的绝对路径
System.out.println(Test.class.getResource("/").getFile());
//指定CLASSPATH文件的绝对路径
System.out.println(Test.class.getResource(cp).getFile());
//指定CLASSPATH文件的绝对路径
File f = new File(Test.class.getResource(cp).getFile());
System.out.println(f.getPath());
}
}
输出:
/D:/projects/bbt/code/cdn/planrpt/out/production/planrpt/
/D:/projects/bbt/code/cdn/planrpt/out/production/planrpt/com/lavasoft/cfg/syscfg.properties
D:\projects\bbt\code\cdn\planrpt\out\production\planrpt\com\lavasoft\cfg\syscfg.properties
Process finished with exit code 0
/D:/projects/bbt/code/cdn/planrpt/out/production/planrpt/com/lavasoft/cfg/syscfg.properties
D:\projects\bbt\code\cdn\planrpt\out\production\planrpt\com\lavasoft\cfg\syscfg.properties
Process finished with exit code 0
总结
使用工程相对路径是靠不住的。
使用CLASSPATH路径是可靠的。
对于程序要读取的文件,尽可能放到CLASSPATH下,这样就能保证在开发和发布时候均正常读取。
-----------------------
推荐资源:
http://www.91ziyuan.com/Html/?904.html
http://shirlly.javaeye.com/blog/218499
附件:http://down.51cto.com/data/2354968
- 本文固定链接: http://qiantao.net.cn/?id=881
- 转载请注明: admin 于 千淘万漉 发表
《本文》有 0 条评论